Deforestation
In 2000, 32% of Haiti’s land was covered in trees, equivalent to 858,000 hectares (858,000 ha).
1 hectare (ha) is equal to:
- 10,000 square meters (m²)
- 0.01 square kilometers (km²)
- 2.471 acres
For comparison, an American Football field covers 1.32 acres. The total forest cover for that time was 2,120,118 acres or 1,606,150 American Football Fields.
From 2001 to 2022, Haiti has lost over 76.4 kHa (76,400 ha) of tree cover, equivalent to 143,018 NFL Fields. Just to emphasize the spectrum, there are only 32 NFL Teams
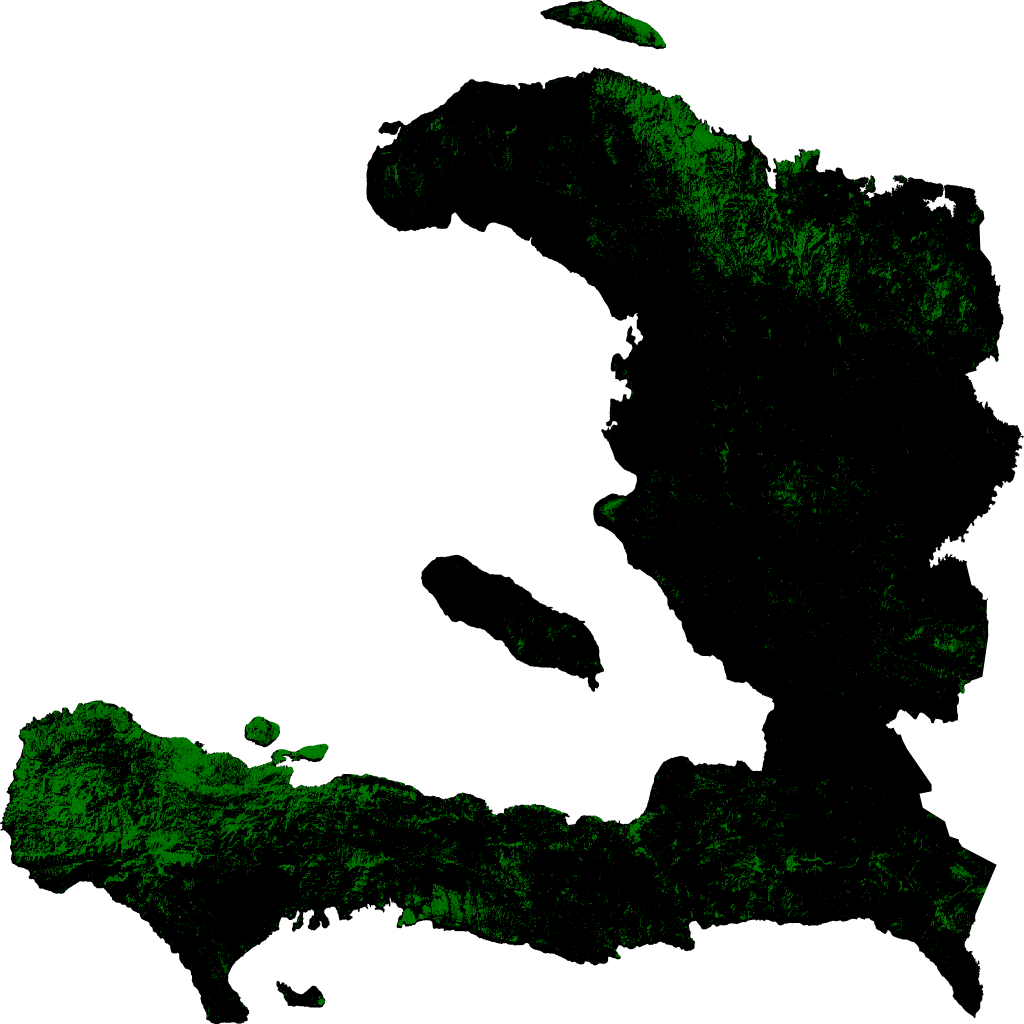
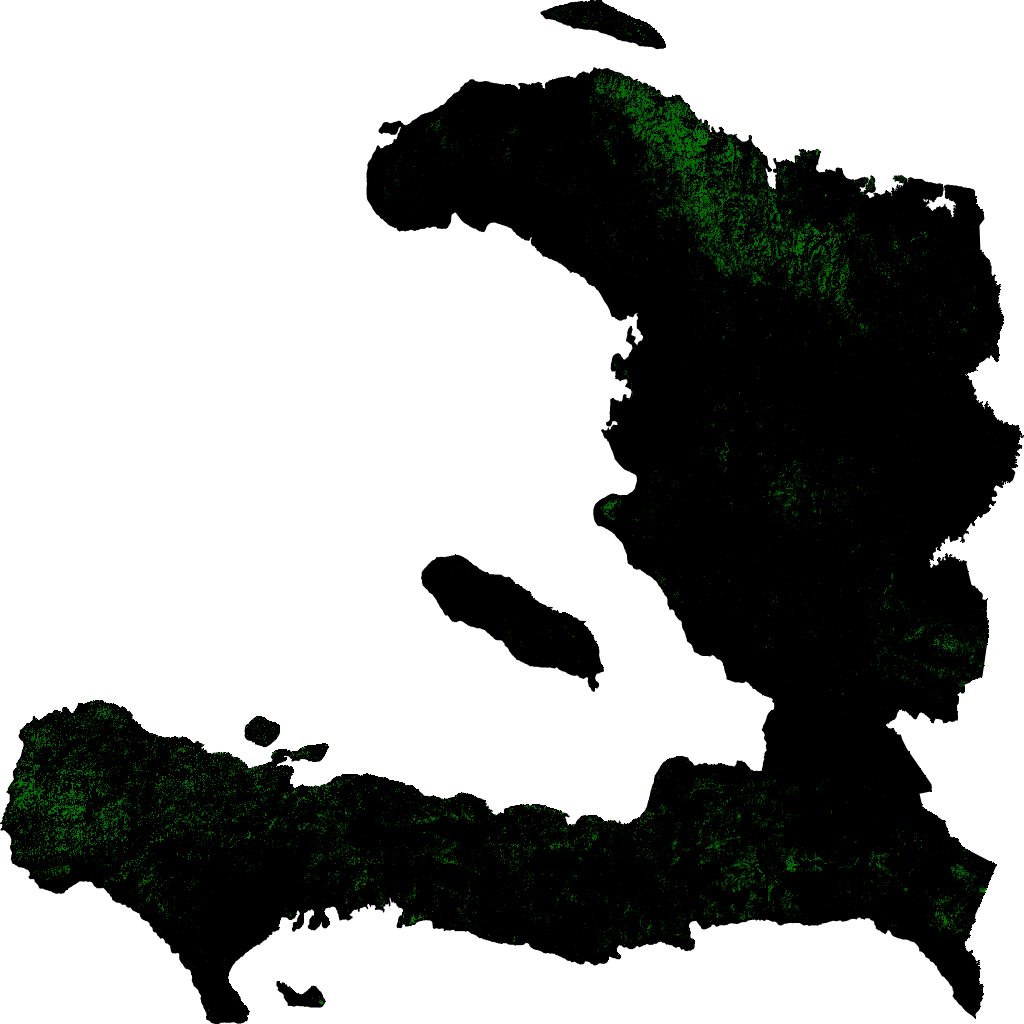
To emphasize the problem, the entire territory size of Haiti is 6,862,997 acres, making the entire country only three times bigger than Yellowstone National Park. However, Haiti has lost tree coverage equivalent to 8.50% of the park area. The size of Yellowstone National Park is 2,219,791 acres, and the forest cover lost in Haiti equals 188,784.4 acres.
In terms of Primal Forest, Haiti has less than 1% left, making it one of the most deforested countries in the world. This alarming trend is expected to result in a mass extinction of endemic species in the next 20 years. As raported by Hedges et al. in “Haiti’s biodiversity threatened by nearly complete lossof primary forest” 2018, only 8 of the 50 mountains in Haiti are still covered in forest; the other 42 are completely deprived of tree cover.
“At the current rate, Haiti will lose essentially all of its primary forest during the next two decades and is already undergoing a mass extinction of its biodiversity because of deforestation” 1
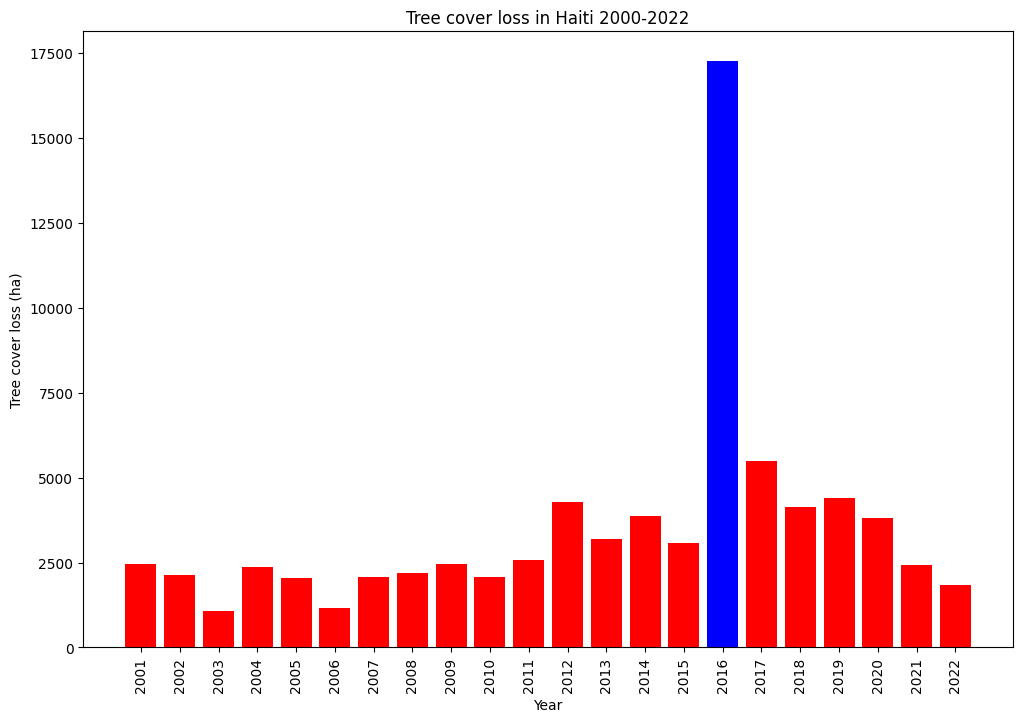
Deforestation of Haiti 2000 - 2022, total forest cover loss, year by year. Dataset used: Hansen Global Forest Change v1.10 (2000-2022)2
“The primary cause of deforestation in Haiti is the overuse of wood for fuel. Almost 70% of the country’s energy needs are met through wood burning, as many Haitians cannot afford alternative fuel sources such as gas or electricity. This high demand for wood has led to the rapid depletion of Haiti’s forests, which has been exacerbated by the country’s weak forest management policies. 3
| Year | Loss (in hectares) | Percentage Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2469.05 | 0.288 |
| 2002 | 2120.38 | 0.248 |
| 2003 | 1070.16 | 0.125 |
| 2004 | 2382.73 | 0.280 |
| 2005 | 2033.24 | 0.239 |
| 2006 | 1162.84 | 0.137 |
| 2007 | 2077.21 | 0.245 |
| 2008 | 2191.55 | 0.259 |
| 2009 | 2464.67 | 0.293 |
| 2010 | 2084.36 | 0.248 |
| 2011 | 2564.21 | 0.306 |
| 2012 | 4272.75 | 0.511 |
| 2013 | 3181.21 | 0.383 |
| 2014 | 3858.87 | 0.466 |
| 2015 | 3087.56 | 0.375 |
| 2016 | 17267.08 | 2.103 |
| 2017 | 5498.83 | 0.684 |
| 2018 | 4131.55 | 0.518 |
| 2019 | 4395.44 | 0.554 |
| 2020 | 3802.06 | 0.481 |
| 2021 | 2413.74 | 0.307 |
| 2022 | 1844.33 | 0.235 |
The most significant deforestation occurred in 2016, resulting in the loss of 17,267.08 hectares of tree cover.
Area deforested in 2016, area with tree loss has been replaced with blue pixels.
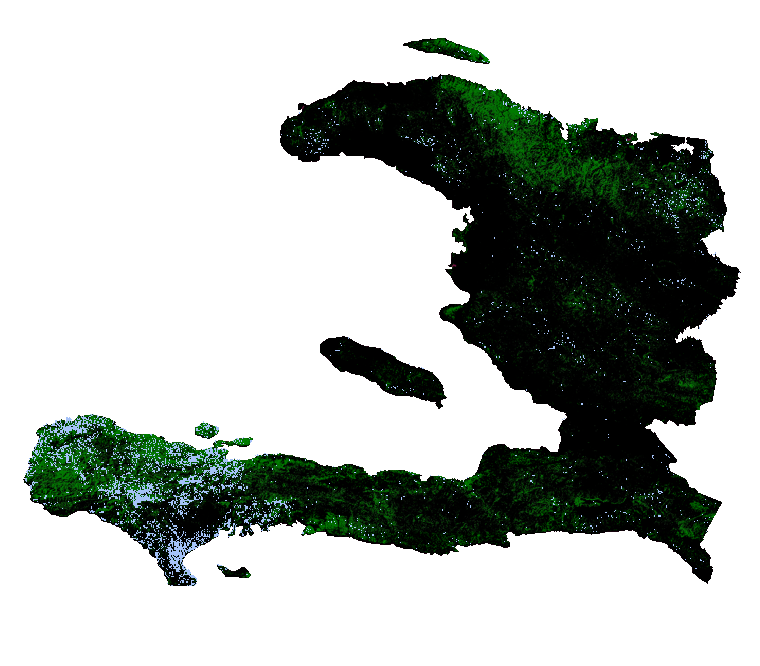
Deforestation between 2000 - 2022, areas with loss has been replaced with blue pixels. Dataset used: Hansen Global Forest Change v1.10 (2000-2022)2
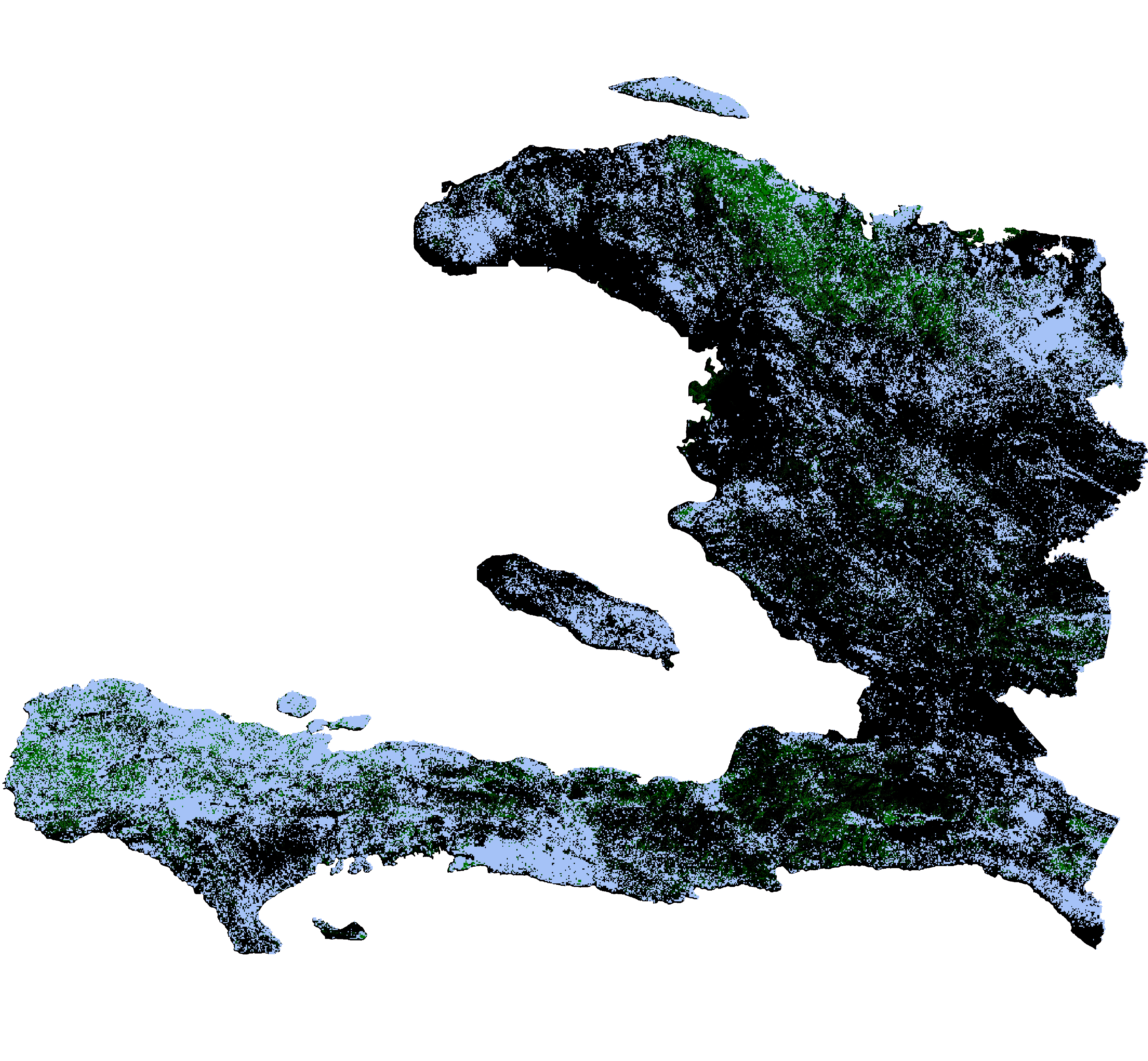
Total tree cover loss 2000 - 2022. Areas with tree loss has been replaced by blue pixels. Download in Full Resolution
Potential solutions include providing financial and technological support to the Haitian people for obtaining sustainable sources of renewable energy. Additionally, educational support can be offered to train Haitian technicians in operating and servicing this technology. Moreover, there is a need for extensive reforestation efforts. While these efforts may not fully replace the losses of primal forest, they have the potential to mitigate erosion and desertification processes to some extent.
Technology and education on modern agrarian methods need to be provided to influence the creation of a sustainable and ecological agrarian industry. Currently, Haiti is dependent on food imports, with the percentage of the value of food imported in total merchandise exports ranging between 103% and 138%.
One factor contributing to sustainability could be the promotion and improvement of crop diversity. This involves planting fruit trees such as mango, avocado, and citrus, and encouraging the local population to trade these products within the community.
Strong policies are essential not only to halt deforestation but also to democratize and bring peace to the people of Haiti. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Democracy Index Report, Haiti scored 2.81 on a scale between 0 and 10, where 0 represents no democracy and 10 signifies full democracy.
“To achieve long-term stability and economic growth, Haiti must establish representative and accountable governance institutions as well as ensure access to justice. While many of Haiti’s governance challenges pre-date the 2010 earthquake, that catastrophe further highlighted the need for an increased focus on governance and government accountability. - United States Agency for International Development” 4
| Year | Food Imports (%) |
|---|---|
| 2000 | NaN |
| 2001 | NaN |
| 2002 | 114.000000 |
| 2003 | 111.000000 |
| 2004 | 108.000000 |
| 2005 | 105.000000 |
| 2006 | 114.000000 |
| 2007 | 122.333333 |
| 2008 | 135.666667 |
| 2009 | 135.000000 |
| 2010 | 132.666667 |
| 2011 | 124.000000 |
| 2012 | 126.000000 |
| 2013 | 132.333333 |
| 2014 | 138.333333 |
| 2015 | 138.333333 |
| 2016 | 133.666667 |
| 2017 | 128.333333 |
| 2018 | 128.000000 |
| 2019 | 132.333333 |
Value of food imports in total merchandise exports in %, compared to developed countries, USA and Germany
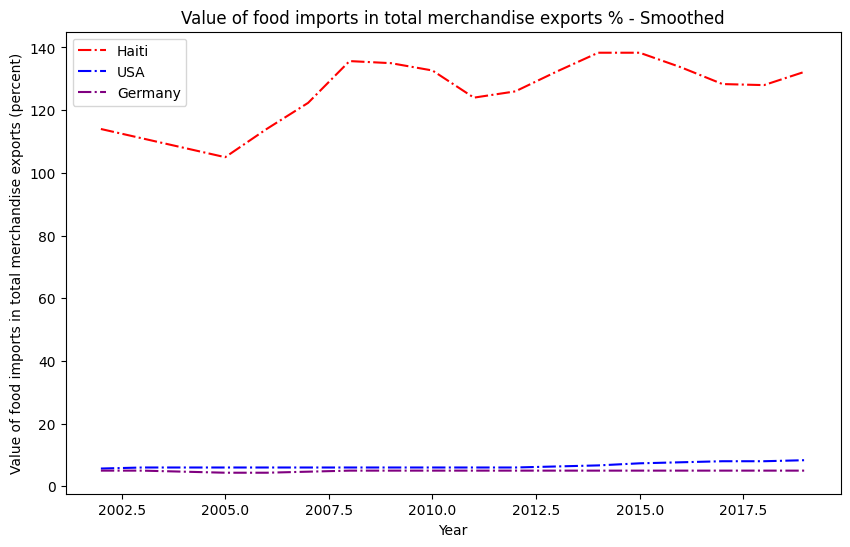
With continuous deforestation, the food crisis is worsening.